230 publications worldwide (including 133 papers, 45 presentations, 22 contributions to journals, 5 demonstrators, 4 keynotes, 2 invited talks, 1 contribution to a book, 1 white paper, 1 patent) in 136 conferences, workshops and journals
Details: https://scale4edge.edacentrum.de/en/publications
Highlights:
1 Patent von UPB: “Enhanced PLL Circuit” (https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2023099639)
5 Best Paper | Keynote Awards (MECO 2025, FDL 2020, DAC 2022 und DATE 2023)
acatech Study „Edge AI: KI nahe am Endgerät. Technologie für mehr Datenschutz, Energieeffizienz und Anwendungen in Echtzeit“ (in German only) by Infineon and TUM with Bosch and University of Tübingen
„Embench™ IOT 2.0 and DSP 1.0: Modern Embedded Computing Benchmarks“ David Patterson et. al. with Co-Autors from Hochschule München University of Applied Sciences in IEEE Computer Volume: 58, Issue: 5, May 2025
Das FZI Forschungszentrum Informatik präsentiert in Kooperation mit dem KIT Chipdesign House Ergebnisse des Vorhabens Scale4Edge auf dem MikroSystemTechnik Kongress 2025. Der Fokus liegt auf skalierbaren Edge-Prozessoren, die eine effiziente Ausführung von künstlicher Intelligenz ermöglichen. Eine anwendungsspezifische System-on-Chip-(SoC)-Plattform, die aus einem RISC-V-Prozessor und einem KI-Beschleuniger besteht, wurde für die effiziente Ausführung einer KI-basierten, kamerabasierten Objekterkennung angepasst. Der Demonstrator dient der Veranschaulichung der in Scale4Edge entwickelten Methoden zur Spezifizierung, Generierung und Verifizierung von Hardware-Eigenschaften im SoC-Entwurf.

Explore the Scale4Edge Eco System at https://scale4edge-new.edacentrum.de/eco-system.
Scale4Edge Projektkoordinator Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Ecker, Distinguished Engineer, Infineon Technologies AG ist zum Digital-Gipfel 2024 der Bundesregierung eingeladen um unter anderem über Scale4Edge und den Projektbeitrag zu "Sicher und resilient in die Zukunft: Innovationen der Mikroelektronik für KI-Anwendungen von morgen" vorzutragen.
Um die immer größer werdenden Datenmengen zu bewältigen, werden Prozessoren benötigt, die nicht nur in puncto Rechenleistung, sondern auch hinsichtlich Energieeffizienz, Zuverlässig keit, Robustheit und Sicherheit höchsten Anforderungen standhalten. Bei einem Speed Geeking können sich die Teilnehmenden zu innovativen Ideen im Bereich KIProzessoren und Open Source informieren und aktuelle Forschungsaktivitäten als Beiträge zu einer technologisch sou veränen Wertschöpfung und Digitalisierung in Deutschland und Europa kennenlernen.
Der Beitrag von Wolfgang Ecker findet am Montag, den 21.10.2024 um 14:30 Uhr statt.
The seemingly endless stream of previously unknown microarchitectural attacks and security flaws in hardware systems is driving the need for more efficient and comprehensive verification techniques. Unique Program Execution Checking (UPEC) is a formal verification methodology that can be used to verify a wide variety of security requirements for hardware at the Register Transfer Level (RTL). With its white-box nature and reusable verification IP, UPEC complements the open-source ecosystem provided by RISC-V. We demonstrate the efficacy of UPEC through a set of selected case studies, covering different threat models and ranging from small RISC-V processors to entire Systems-on-Chips (SoCs). Details and slides.
The video is played on YouTube if you click on the image below.
Aus Aus Industry.zero & Transformation for Industy Leaders am 9.7.2024 am 9.7.2024
Die jüngsten Erfolge in der generativen KI basieren auf einem Anstieg zentral verarbeiteter Daten, größeren neuronalen Netzen und mehr Rechenkapazität. Dies wirft Fragen zu Datenschutz, Kosten und Ressourcenverbrauch auf. Daher wird parallel ein anderer Ansatz verfolgt: die Dezentralisierung von KI-Architekturen nach dem Vorbild des Edge Computing – genannt Edge AI. Das Ziel: Daten nahe am Nutzenden und nicht in der Cloud verarbeiten. Wolfgang Ecker, Distinguished Engineer bei Infineon Technologies und Honorarprofessor der TU München, erklärt Vorteile, Einsatzmöglichkeiten und aktuellen Hürden von Edge AI.
Im Rahmen des RISC-V Summit 2024 wird die erste Scale4Edge-Roadshow durchgeführt.
Scale4Edge Partner präsentieren Poster, Vorträge und Demonstratoren.
Die Scale4Edge-Partner stehen für persönliche Gespräche bereit. Bitte vereinbaren Sie Termine mit Andreas Vörg <voerg![]() edacentrum [dot] de>
edacentrum [dot] de>
Power-efficient edge AI applications have an enormous market potential. Key factors for a competitive hardware solution in this domain are energy efficiency and low silicon area in relation to computing performance. SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH is closely collaborating with TU Dresden in this domain for transferring cutting-edge research and development on AI hardware accelerators into commercially viable applications.
Within the Scale4Edge project, TU Dresden has developed the SpiNNedge AI accelerator IP for audio keyword spotting applications and beyond. Key focus of SpiNNedge is the reduction of on-chip memory and processing effort by hardware-optimized preprocessing and exploitation of sparsity in neural network based classification. With on-chip memory being one of the core drivers of silicon area and static power, SpiNNedge helps to significantly improve in both factors.
But an AI accelerator alone is worth almost nothing in isolation. Integration in the Scale4Edge ecosystem made SpiNNedge useable and created a commercial potential. The Scale4Edge RISC-V ecosystem core by MINRES runs the application with an offloading of key processing tasks for keyword spotting to the SpiNNedge accelerator. The customizable RISC-V core solution could be perfectly adapted to the needs of the keyword spotting application. Moreover, Scale4Edge made a joint effort to provide software support for hardware extensions of microcontrollers in the widely adopted machine learning compiler Apache TVM. This is highly beneficial for the useability of an accelerator like SpiNNedge, as it bridges the gap between hardware IP and high-level software frameworks for machine learning that users employ to develop their edge AI applications.
TU Dresden has successfully implemented a test chip for audio keyword spotting, integrating the SpiNNedge accelerator with a customized MINRES RISC-V core into an overall processing chain from microphone input to detected keywords. The chip realizes a hierarchical processing approach, first detecting speech in the microphone input, and then starting keyword classification. Speech detection is performed by the ZEN accelerator module, which won a 1st prize in the BMBF German innovation competition "energy efficient AI systems". The chip has been implemented in GlobalFoundries 22 FDX technology, employing adaptive body biasing (ABB) IP for leakage power reduction, developed and provided by Racyics, a spin-off of TU Dresden.
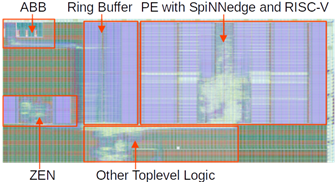
Figure 1: Core Layout of the keyword spotting test chip by TU Dresden. Core part is the processing element (PE) with TU Dresden's SpiNNedge accelerator and the MINRES RISC-V core.

Figure 2: Demo board for keyword spotting with the test chip by TU Dresden (white, center)
The processing element with the MINRES RISC-V core and the SpiNNedge accelerator performs real-time keyword spotting in 34 uW, achieving a classification accuracy on the widely-used Google speech command dataset of over 95%, which outperforms most of the existing low-power hardware solutions for this use case. A demo board has been implemented to showcase the solution.
The mission of SpiNNcloud Systems is to design energy-efficient AI systems by leveraging practical inspiration from the brain. Its core product is a holistic computing solution ranging from chip design, software development to deployment of full data center servers. Despite our large-scale supercomputers being built leveraging Arm IP, our constant commitment to pursue innovation in an Edge2cloud continuum has led us to evaluate different solutions at different scales. SpiNNcloud is highly interested in commercializing Edge AI solutions, in which the Edge IP built in Scale4Edge stands as a clear and attractive building block. The flexibility of these custom-extended RISC-V cores allow a path to achieve ultra efficient operations at the edge. Furthermore, the Scale4Edge Ecosystem provides a quick start for us into an efficient Edge exploration including know-how from compilers, functional safety, ISA-extensions and chip design methodology among others. Additionally, it introduces us to a wide variety of best practices that can boost development speed and reduce technical risks, all crucial to ensure commercial success. Strategically the consortium enables a fully European ecosystem, especially a German one, with technological independence that increasingly becomes more important to protect and foster companies in the field of computing.
Cont@ct:
TU Dresden | Dr.-Ing. Johannes Partzsch | johannes [dot] partzsch![]() tu-dresden [dot] de
tu-dresden [dot] de
MINRES | Eyck Jentzsch | eyck![]() minres [dot] com
minres [dot] com
SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH | Matthias Lohrmann | matthias [dot] lohrmann![]() spinncloud [dot] com
spinncloud [dot] com
https://www.edacentrum.de/scale4edge/
Further Scale4Edge partners and sub-contractors
Die Partner der BMBF-ZuSE-Projekte KI-Mobil, KI-Power und Scale4Edge freuen sich darauf, sie in Kaiserslautern zu treffen!
Teilnahmeregistrierung: https://eveeno.com/130451080
| 16:00 | Eröffnung Grußwort Einordnung in ZuSE |
| 16:20 | „Die Rolle von Prozessoren bei den europäischen/deutschen Bemühungen um Halbleitersouveränität - Herausforderungen und Chancen” Impulsvortrag Prof. Norbert Wehn, RPTU Podiumsdiskussion Moderator: Prof. Wolfgang Nebel, edacentrum Teilnehmer: Mario Brandenburg, parlamentarischer Staatssekretär BMBF Prof. Armin Dietz, Technische Hochschule Nürnberg, Projektkoordinator KI-Power Prof. Wolfgang Ecker, Infineon, Projektkoordinator Scale4Edge Eyck Jentzsch, MINRES Technologies GmbH Dr. Hans-Jörg Vögel, BMW Group, Projektkoordinator KI-Mobil |
| 17:30 | Pause |
| 17:45 | Projektvorstellungen Prof. Wolfgang Ecker - Scale4Edge Dr. Hans-Jörg Vögel – KI-Mobil Prof. Armin Dietz – KI-Power |
| 18:45 | Poster und Demos aus den ZuSE Projekten mit Stehempfang |
| 19:45 | Gemeinsames Abendessen im Fritz Walter Stadion |
| 22:00 | Ende der Veranstaltung |